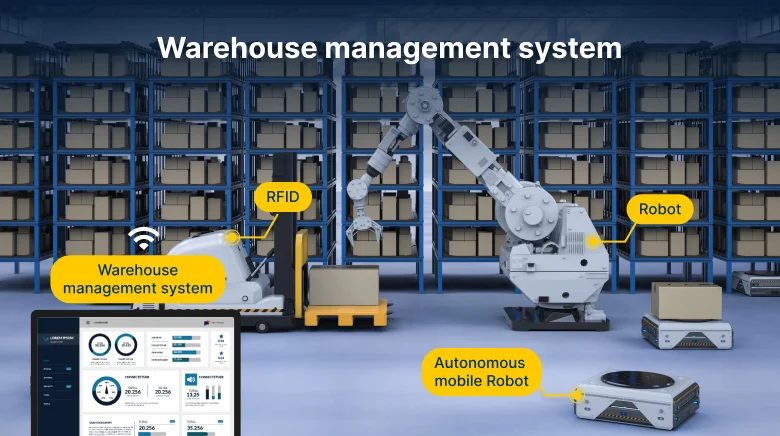
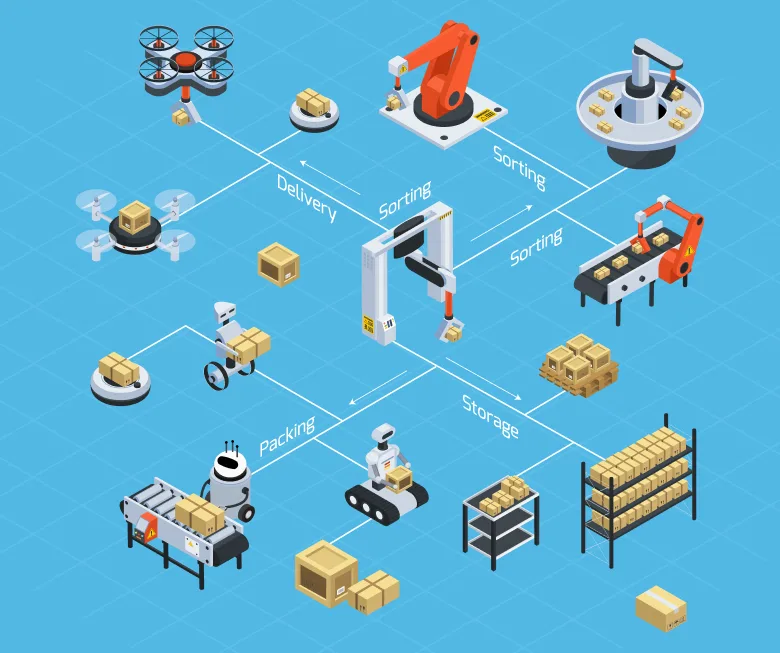
Manual warehouse processes are time-consuming, prone to error, and hard to scale. As customer demands grow and supply chains develop, companies are adopting warehouse automation to improve speed, accuracy, and efficiency. From order picking and packing to inventory tracking and data management, automated warehouse technology is changing the way warehouses operate.
Warehouse automation is about replacing repetitive, human-intensive work with intelligent systems and technology. With the right warehouse automation systems in place, businesses can minimize labor expenses, decrease errors, and accelerate order fulfilment. Software-based digital warehouse transformation is allowing businesses to keep up with a quickly evolving market.
This blog explores what warehouse automation really means, how it works, and the benefits it offers. We’ll also guide you through the warehouse automation process, types of technologies involved, and how to identify the right time for automation.
What is warehouse automation?
Warehouse automation is the process of automating repetitive operations involved with inventory moving in and out of a warehouse, distribution center, micro-fulfillment center, or retail facility through equipment, robotics, or software. Warehouse automation simplifies inventory management. By minimizing overhead and accelerating fulfilment, distribution, and replacement, it enhances overall efficiency. The outcome is better throughput and smoother operations.
Automation can be basic or moderately sophisticated, from bar-code scanning to self-driving robots that support employees with moving goods or getting products ready to ship. Using automation can reduce worker fatigue, injury, and mistakes, if done properly. It also frees up staff to focus on higher-value tasks that require judgment or problem-solving.
How does warehouse automation work?
Warehouse automation uses technologies such as robotics and sensors, along with software like inventory management systems, to automate operations. Warehouse automation streamlines receiving, storing, and retrieving goods using sensors and smart inventory systems.
It aligns business-critical processes in your warehouse with customer demand. It begins with a Warehouse Management System (WMS) that automates data capture and manual processes, inventory control and supports data analysis. These systems are integrated with other solutions to manage and automate tasks effectively across various business and supply chain functions.
Digital automation employs data and software to minimize manual processes and eliminate human mistakes. For instance, automatic identification and data capture technology like RFID and mobile barcode scanning.
Advantages include integration with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, increased security, improved efficiency of data management, minimum operational and legal risk, and increased safety. Furthermore, digital automation can improve employee experience, customer service, and lower operational expenses related to error fixation.
Physical automation is an approach to using technology, including robots, to reduce employee movement and create more effective workflows. The benefits of physical automation are improved warehouse capacity and productivity, increased reliability and scalability of services, and better performance.
What are the benefits of warehouse automation?
The real value of warehouse automation lies in redesigning operations for long-term success. Automation gives you the ability to achieve benefits that support both day-to-day performance as well as business agility:
-
Enhanced efficiency and throughput
With warehouse automation systems in place, tasks are completed faster and with greater accuracy. This means goods move through the warehouse more quickly, allowing you to handle higher order volumes without adding extra labor.
-
Greater order fulfilment accuracy
Automated warehouse solutions minimize picking and packing errors by guiding workers to complete tasks. This level of precision improves customer trust and reduces returns.
-
Better supply chain agility
By integrating warehouse automation technology with inventory and shipping systems, your operations can respond quickly to demand changes. This responsiveness allows you to satisfy customers’ demands and adapt to shifts in markets or supply chain disruptions.
-
Improved inventory security and visibility
Smart warehouse solutions and tracking tools provide real-time visibility of stock levels. This mitigates loss or theft risk, enhances control over inventory, and enables smoother digital transformation of the warehouse with improved decision-making information.
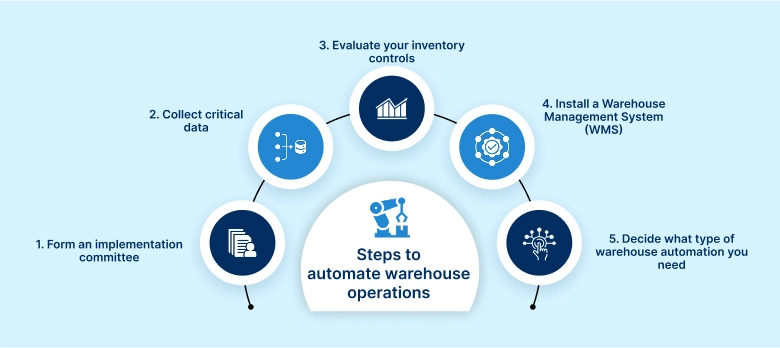
5 steps to automate your warehouse operations
Implement warehouse automation in phases to handle complexity, link to operational objectives, and maintain long-term scalability. Focus on a clear roadmap that supports your business requirements and long-term growth. Having a systematic approach also helps you to steer clear of costly mistakes and make your shift towards smart warehouse solutions yield measurable gains.
-
Form an implementation committee
Set up a committee of internal stakeholders with knowledge of existing warehouse performance, capabilities, and issues, and awareness of existing gaps in technology. Engage third-party professionals with hands-on experience in your industry, warehouse operations, and supply chain automation.
-
Collect critical data
Successful warehouse automation depends on data about your existing supply chain and important warehouse operations. Evaluate your current data collection method and infrastructure before implementing new automation technology. You can allocate this responsibility to experienced automation service providers.
-
Evaluate your inventory controls
Inventory control is at the core of warehouse operations. Prior to installing a warehouse automation solution, define or standardize your Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for inventory control. Establish SOPs for purchase, shipping, receipt, customer satisfaction and inventory loss. Identify the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) used to assess the effectiveness of automated inventory control procedures. Review the current method of inventory accounting in use and establish how automation will affect it.
-
Install a Warehouse Management System (WMS)
WMS have software modules that assist with controlling and tracking inventory, warehouse operations, minimizing labor costs for manual operations, and enhancing customer service. A contemporary WMS is optimized for mobile devices and must be compatible with your current enterprise software.
-
Decide what type of warehouse automation you need
Do you want to use automation to digitize manual data entry and lower labor expenses related to back-office warehouse functions? Or you want to increase warehouse space and add locations? Identifying will depend on your business goal and operational challenges. And it will help align investments with goals and drive scalable, efficient operations.
Types of warehouse automation technology
Selecting the optimal warehouse automation technology is all about fixing your specific operational issues. Evaluating all options for scalability, integration capability, and ROI, you can invest in solutions that are not only meeting today’s requirements but also scale with your future growth.
-
Goods-to-Person (GTP)
Goods-to-person fulfilment is one way to make operations more efficient and less congested. It manages conveyors, carousels and vertical lift in the warehouse. The right implementation can double or triple the pickup rate in a warehouse.
-
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
AS/RS is a technology for GTP fulfilment that comprises automated equipment and systems such as material-carrying vehicles, mini-loaders and tote shuttles for storing and retrieving materials or goods. Space-saving warehouse applications with high volumes tend to employ AS/RS systems.
-
Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
This mechanized automation class has nominal onboard computing power. AGVs follow a prescribed path through the warehouse using magnetic strips, wires or sensors. AGVs can only accommodate large, straightforward warehouse environments that are planned with this path layout. AGVs do not suit complicated warehouses that have a lot of human traffic and limited space.
-
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
AMRs are more agile than AGVs. They employ GPS systems to map efficient routes across the warehouse. They use sophisticated laser guidance systems to identify obstacles. AMRs can travel safely in dynamic environments with high levels of human traffic. They are simple to program with routes and easy to implement quickly.
-
Pick-to-light and put-to-light systems
These systems incorporate handheld barcode scanners synchronized with digital light displays that guide warehouse pickers where to put or take out chosen items. They significantly lower walking and searching time, and human error in high-volume environments.
-
Voice picking and tasking
Voice-directed warehouse procedures, or pick-by-voice, utilize speech recognition software and wireless headsets. The system develops optimized pick paths to instruct warehouse employees where to pick or put an item away. This technique eliminates the use of handheld devices such as RF scanners so pickers can focus on the task with better safety and efficiency.
-
Automated sortation systems
Sortation refers to the act of locating items on a conveyor system and directing them to a warehouse location through RFID, barcode scanners, and sensors. Automated sortation systems are utilized by businesses in order fulfilment for receiving, picking, packing, and shipping.
Which warehouse functions can be automated?
Automation can touch nearly every facet of warehouse operations, but the real value comes in choosing which areas will benefit the most. Let’s take a look at the areas:
-
Receiving
You can use mobile devices in receiving areas of your warehouse to quickly capture data. Integrated software captures, processes, and stores data influencing downstream and upstream automated processes.
-
Returns
You can automate return using sorting devices and equipment such as conveyors. Utilize them to sort products into return-to-stock shelves or store in assigned storage locations.
-
Putaway
Putaway is the movement of product from receiving into storage. Digital automation of warehouse processes can make putaway faster and more precise. You can automate this process to enable cross-docking, where merchandise is quickly sorted and processed and loaded onto trucks for shipment to various destinations rather than being put away into the warehouse.
-
Picking
Manual order picking is the most expensive warehouse operation. Warehouse travel time can use as much as 50% of working hours. You can use GTP system applications to quickly enhance the speed and efficiency of traveling inventory from stock locations to fill customer orders.
-
Sorting
Sorting and warehousing consolidation of inventory is a time-consuming, function. Employ automatic sortation and AS/RS technology to enhance inventory accuracy and quality assurance by identifying and processing small or delicate inventory items as a distinct unit.
-
Replenishment
Automated tracking of inventory and cycle counting facilitate automated reorders. Once an item reaches the predetermined par level, the system automatically places an order request and indicates that it needs to be approved. Computerized replenishment has the potential to avoid overstocking charges and inventory loss due to spoilage and theft.
-
Packaging
This phase is vital because packaging material is high in cost. Packaging and cartonization systems automate determining the optimal shipping packaging type by utilizing product characteristics such as durability, size, and material price.
-
Shipping
Shipping systems automate using conveyors, scales, dimension detectors, printers and applications software to calculate available carriers, estimate shipping costs and print out labels on packages to be shipped.
When should you automate your warehouse?
Automate your warehouse when operational inefficiencies start limiting growth or customer satisfaction. You must watch early for these indicators to transition smoothly before challenges become costly.
Answer these questions before committing to warehouse automation projects:
-
Are your orders delayed due to a limited workforce?
-
Are your existing warehouse processes labor-intensive?
-
Are your inventory levels inaccurate?
-
Are you working with aged warehouse management software or manual tools?
-
Do you need to upsize/downsize staff to manage changing demands?
-
Do you need to boost productivity or process more shipments?
-
Are you out of storage or making inefficient use of your existing storage space?
Warehouse automation requirements
Warehouse automation is very valuable, and companies must take the time to carefully examine their operations prior to taking the step. Effective implementation of warehouse automation begins with a strong foundation.
-
Large number of repetitive tasks
Warehouses with a high number of repetitive, routine tasks, for instance, picking, packing and shipping orders, must implement automation. Automation systems have the capability to run 24/7, reducing waste and allowing personnel to concentrate on more sophisticated, value-added jobs.
-
Standardized processes
Automation performs best in highly standardized process environments. Tasks such as order processing, putaway and replenishment of inventory can be automated with ease, if the business has well-documented, consistent procedures.
-
Scalability needs
Companies that grow fast and experience increasing order volumes may need to expand the business at a rapid pace. Automating key processes can assist them in meeting increased throughput and demand without raising the headcount.
-
Requirement of consistency and accuracy
Warehouse automation makes things consistent by doing the job the same way all the time. This removes the possibility of human error and enhances inventory accuracy, order picking and order fulfilment.
Expected outcome by automating warehouse operations
Automation is about upgrading equipment and creating more agile and responsive operations. Knowing the tangible changes, you can expect help in setting realistic goals and measuring success. This perspective allows you to track the true benefits of warehouse automation and see how it drives both performance and long-term savings.
| Process | Before automation | After automation | Expected outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Order picking | Staff searched shelves manually using printed lists, leading to slow and error-prone picking. | Automated warehouse solutions like pick-to-light and mobile robots assist or fully automate picking. | Faster picking, minimized human error, improved order accuracy, and better staff productivity. |
| Inventory management | Inventory was tracked using spreadsheets or paper logs, often leading to stockouts or overstock. | Warehouse automation software enables real-time tracking with barcode/RFID scanning and dashboards. | Improved stock accuracy, lower carrying costs, and better demand forecasting. |
| Receiving and putaway | Items were manually sorted and stored, causing delays and misplacements. | Intelligent warehouse systems automatically sort, label, and direct items to optimal storage zones. | Faster putaway, better space utilization, and reduced labor hours per inbound shipment. |
| Shipping and packing | Staff packed and labeled shipments manually, risking wrong or delayed deliveries. | Warehouse process automation handles sorting, packaging, and label printing. | Increased shipping speed, fewer returns, and enhanced customer satisfaction. |
| Reporting and analytics | Manual data entry led to delays in performance tracking and decision-making. | Digital warehouse transformation integrates real-time analytics and automated reporting tools. | Faster insights, better visibility, and more agile decision-making. |
| Returns processing | Returns were handled manually, with inconsistent tracking and delays in restocking. | Warehouse automation systems streamline reverse logistics with clear routing and automated updates. | Quicker turnaround, improved customer experience, and higher recovered value from returned goods. |
| Labor allocation | Staff assignments were planned manually without insight into workload fluctuations. | Smart warehouse solutions dynamically allocate tasks based on demand and availability. | Optimized labor usage, reduced overtime, and balanced workloads across shifts. |
Let’s restructure the operations of your warehouse
Embracing smart warehouse solutions is about building a more agile, scalable, and data-driven operation. The right warehouse automation technology helps you make better decisions, increase visibility, and gain a competitive edge. Whether you’re planning a full transformation or starting small, taking the first step in the warehouse automation process today can provide long-term success. Let your journey to digital warehouse transformation begin now, with the right strategy and partner.
FAQs
1) How much does it cost to automate a warehouse?
The cost of warehouse automation can vary widely based on your warehouse size, current infrastructure, and the level of automation you choose. It’s best to consult with experts to assess your specific needs and determine a tailored budget. To discuss your warehouse automation requirements, connect with our experts.
2) Which warehouse automation technology is best for small and medium-sized warehouses?
For small to mid-sized operations, modular warehouse automation systems like mobile robots, conveyor belts, and cloud-based warehouse automation software offer cost-effective and scalable solutions without major disruptions.
3) How long does it take to implement warehouse automation?
Depending on the complexity, a warehouse automation implementation can take anywhere from a few months to over a year. Smaller systems may be up and running in 3–6 months, while full-scale projects take longer due to planning, integration, and testing.
4) Will automation reduce the need for warehouse staff?
Not entirely. While intelligent warehouse systems reduce manual tasks, they often shift staff responsibilities toward supervision, system monitoring, and exception handling. Automation supports teams rather than replacing them.
5) How do I choose the right automation partner or vendor?
Start by looking for a vendor with experience in logistics warehouse automation, a strong portfolio of scalable solutions, and the ability to integrate with your existing systems. The right partner will not only understand your operational goals but also guide you through a smooth warehouse automation implementation.
6) Can warehouse automation integrate with my existing ERP or WMS system?
Yes, most modern warehouse automation technologies are designed to integrate seamlessly with ERP and WMS platforms. This allows for unified data flows, better inventory control, and smoother overall operations.
7) How secure and reliable are automated systems?
Today’s automated warehouse solutions use advanced security protocols and backup systems to ensure data protection and operational stability. With regular updates and monitoring, they are both secure and highly reliable.
8) What’s the difference between full and partial warehouse automation?
Full warehouse automation replaces most manual processes using robotics, AI, and software. Partial automation focuses on specific tasks like picking or packing, allowing gradual adoption and lower initial investment.
9) What are the maintenance requirements of an automated warehouse?
Warehouse automation systems require periodic software updates, equipment calibration, and preventive maintenance. A solid support plan and trained staff ensure smooth operations and minimal downtime.