AI agents are autonomous software systems designed to perform tasks, achieve specific goals, and learn and adapt from continuous feedback received. They interact with their surroundings, gather information, and use this data to achieve goals set by humans.
These AI agents contribute significantly to drive value across industries. Businesses incorporate different types of AI agents to streamline operations and drive data-informed decisions. By adopting an agentic AI service, organizations can deploy tailored AI agents that integrate seamlessly into workflows, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs.
Organizations using GenAI–enabled customer service agents saw a 14% increase in issue resolution per hour and a 9% reduction in time spent handling issues – McKinsey & Company
In this blog post, we will explore what an AI agent is, how they work, different types, real world use cases, how Needle helps business and future AI trends.
What are AI agents?
AI agents are autonomous software programs that use artificial intelligence to perform tasks on behalf of users. These agents use machine learning and large language models to perceive the environment, make decisions, and achieve specific goals.
AI agents can process multiple forms of information like text, voice, code, and more. They use AI to learn and adapt from real-time feedback and changing conditions. These AI agents range from simple rule-based systems to advanced learning algorithms to refine their behavior. They also work with other agents to coordinate and perform more complex tasks.
For instance: AI agents in the finance sector monitor and analyze financial transactions in real-time to detect fraudulent activities. These agents identify anomalies, block suspicious transactions and alert teams about potential fraud. Thus, enabling the team to enhance security and compliance regulations.
How do AI agents work?
AI agents work by simplifying complex tasks. Advanced AI agents follow structured processes when processing input, analyzing data, making decisions and executing action while continuously learning from the experience. Here is an overview of how AI agents work:
-
Perception
An AI agent begins the process by gathering information from the surrounding. This data could include user input, accessing digital data or sensor data. The perception model converts raw data into a form that AI agents can understand and process.
For instance, an autonomous car gathers information about object detection using cameras and radar.
-
Decision making
Once the data is collected, the AI agent analyzes it to take the next step. These AI agents use:
- Natural language processing to evaluate input
- Sentiment analysis to evaluate the tone and input
- Classification algorithms to make decisions by choosing the best course of action
It also plans a sequence of steps or future outcomes.
For instance, an AI agent while handling a customer support ticket can evaluate tone and context to decide whether to handle it immediately or escalate it to a human agent.
-
Action
After a decision is made, the AI agent takes the next step by acting on the decision taken to achieve the specific task. This action could include sending messages, updating the data, triggering alerts or sending commands to other systems.
For instance: An AI agent, while handling a support ticket, can flag it for immediate human attention or automated troubleshooting steps.
-
Learning and adaptation
Advanced AI agents take actions, evaluate them and then learn and adapt from the feedback received. This process is also called reinforcement learning. It allows AI agents to refine their response over time.
For instance: AI agents learn from support solutions, success rates and customer satisfaction scores. It treats each situation as a learning opportunity to improve its future response and routing decision.
What are the different types of AI agents?
AI agents are categorized based on their level of decision-making process and how they interact with their surroundings. Some AI agents’ function on predefined rules, while others use algorithms to refine their response.
Understanding the different types of AI agents helps businesses select the most appropriate agentic AI service for various real-world problems and applications. Let’s explore the five main types of agents in AI:
-
Simple reflex agents
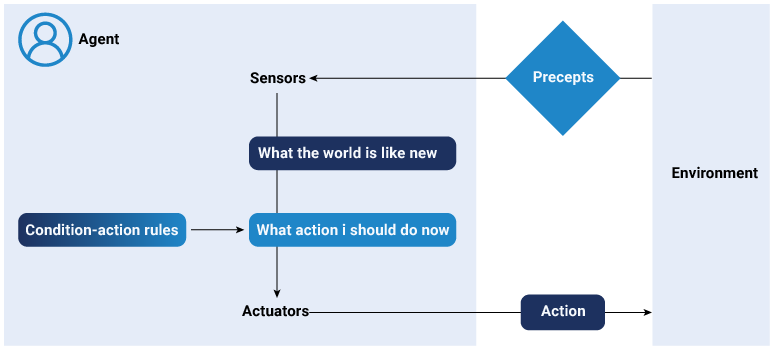
These AI agents are designed to function based on the direct response to the environment. Simple reflex agents make decisions based solely on their current sensory input. They respond immediately to surrounding stimuli without needing memory or learning processes. These agents follow predefined rules to make decisions. It does not consider past or future experience.
For instance, a thermostat is a simple reflex agent that turns the heater on and off based on the current temperature.
-
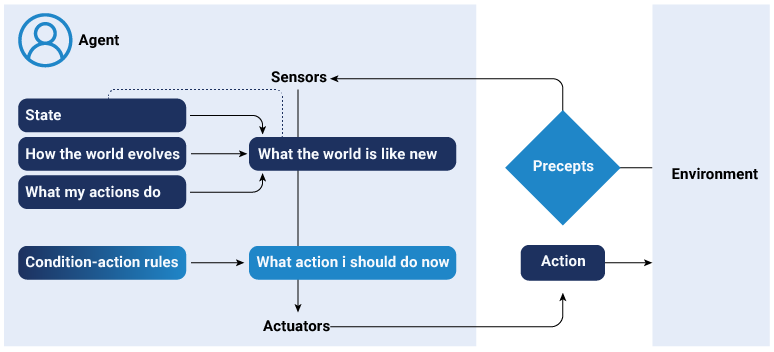
Model-based reflex agents
These AI agents are the advanced version of simple reflex agents. A model-based agent has more advanced decision-making capability. While this model responds solely to current sensory input, it also uses internal models to understand the environment’s dynamics and make decisions accordingly. Instead of following specific rules, a model-based agent evaluates potential outcomes and their consequences before making any decision.
For instance, Waymo, a self-driving car company, uses sensor cameras and AI systems to navigate roads in cities. The car’s perception system works as a model based reflex agent. It uses sensor data and detailed maps to provide the AI system with information about the car’s location and surroundings.
-
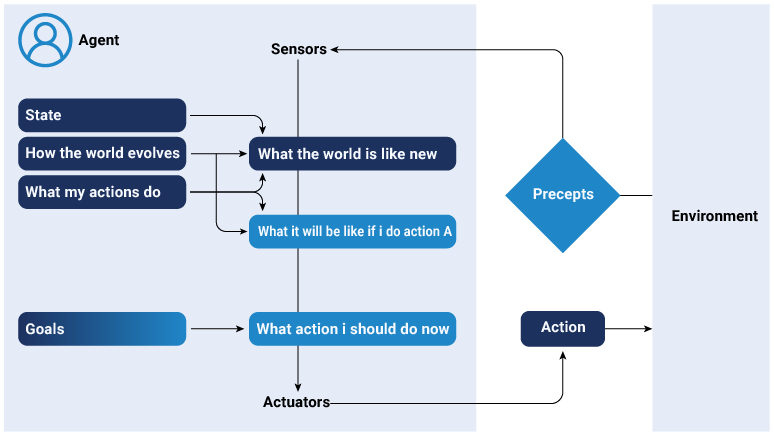
Goal based agent
These agents are intelligent and operate by setting clear goals and making plans to achieve them. Goal-based agents evaluate their current state, future consequences and evaluate possible actions that drive desired outcomes. They plan a series of actions to achieve the set goal. Moreover, they use planning and search algorithms to find an appropriate sequence of action that can help achieve the goal.
For instance, a robot is designed as a goal-based agent to navigate a building. It might set a goal to reach the topmost room of the building. It uses logical reasoning to plan a path that minimizes errors and avoids obstacles, thus achieving the goal effectively.
-
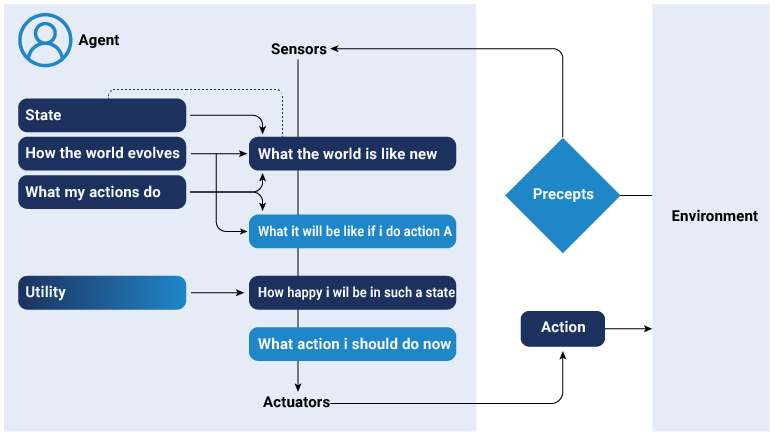
Utility based agent
Beyond achieving goal, these agents function with the awareness of utility. They use utility functions to evaluate and select actions that can enhance efficiency and provide benefit. Utility-based agents are effective in dynamic and complex environments. They choose actions that enhance their utility, considering both the goal and the desirability of the resulting state. They balance competing objectives and adapt to changing conditions. Moreover, they are also suited for scenarios that require a balance between multiple competing objectives.
For instance: A stock trading bot not only sets a goal to achieve profit but also implements a utility factor that minimizes risk, balancing the two factors.
-
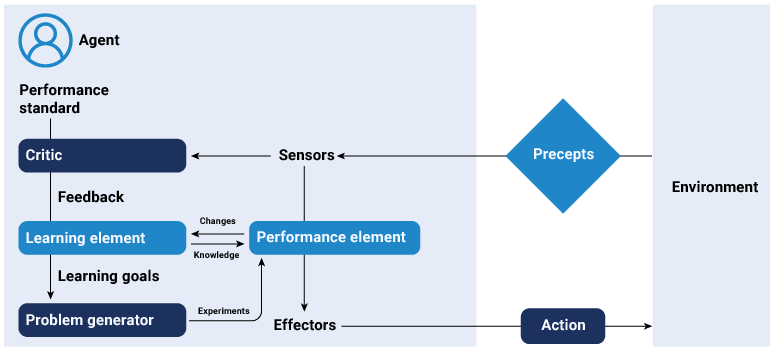
Learning based agent
These agents have the ability to learn from interactions and experiences and improve their performance over time. Learning based agents continuously improve their performance based on the feedback received. This learning capability allows them to enhance their decision-making ability and perform better in complex and uncertain situations.
For instance, a customer support AI agent identifies correct actions through appreciation and incorrect ones through penalties. With time it identifies which actions maximize customer satisfaction and enhances its approach accordingly.
Table comparing AI agent types:
To understand how different types of AI agents function, let’s compare their key features. The following table compares AI agents based on their definition, examples, adaptability, strengths and limitations.
| Criteria | Simple reflex agents | Model-based reflex agents | Goal-based agents | Utility-based agents | Learning agents |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agents that act solely based on the current percept, ignoring history. | Agents that maintain an internal model of the environment to make decisions. | Agents that act to achieve specific goals, evaluating actions against those goals. | Agents that select actions based on both goals and the utility (value) of outcomes. | Agents that improve their performance over time by learning from experiences |
| How it works | Uses condition–action rules to respond directly to inputs. | Combines current percepts with stored information about past states to choose actions. | Evaluates possible actions by determining if they help achieve the goal. | Weighs different actions by calculating outcomes which leads to the overall benefit. | Uses data and feedback to adapt decision-making strategies. |
| Example | The thermostat turns heat on/off based on temperature. | Robot vacuum navigating around obstacles based on prior map data. | GPS system that helps find routes to a destination. | Recommendation system choosing content with highest predicted user satisfaction. | Fraud detection system improving accuracy through new transaction data. |
| Memory of past states | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Adaptability | Low | Moderate | High | High | Very high |
| Environmental suitability | Static and fully observable environments. | Partially observable and predictable environments. | Dynamic environments with clear objectives. | Complex environments requiring trade-offs. | Evolving environment with continuous learning. |
| Strengths | Fast, simple, low computation needs. | Handles incomplete information better than simple reflex agents. | Goal-directed and flexible. | Optimizes decisions for best outcomes. | Continuously improves performance. |
| Limitations | Cannot handle changes or incomplete data. | Limited adaptability without goal awareness. | Requires goal definition; may ignore other beneficial outcomes. | Needs accurate utility measures; can be complex to implement. | Requires training data and time to learn effectively. |
What are the benefits of adopting AI agents?
Adopting AI agents can redefine how your business operates. From enhancing decision-making with real-time insights to improving customer experiences and streamlining workflows, AI agents offer tangible advantages. These translate into efficiency, cost savings, and competitive growth.
-
Increased productivity
AI agents automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human agents for more strategic work. They process information and respond to requests faster than humans, thus enhancing productivity and reducing bottlenecks.
-
Enhanced accuracy
AI agents analyze information, identify patterns and make data-driven actions. This results in accurate decision making that is required to achieve specific tasks. Agents exchange information within their environment, thus enhancing quality of response and accuracy.
-
Personalization
Using input data, AI agents can offer personalized services whether it is shopping preferences or healthcare treatment plans. They enable organizations to provide customized solutions by analyzing customer behavior and buyer journeys. Thus, enhancing customer satisfaction and retention rate.
-
Task automation
Organizations are adopting generative AI and machine learning technologies to optimize and automate workflow. AI agents automate complex processes that would otherwise require human agents. These advancements enable organizations to achieve goals rapidly and at scale, without human intervention.
What are the real-world use cases of adopting AI agents?
AI agents are making a measurable impact across industries. They turn complex challenges into streamlined solutions. From automating customer support to optimizing energy resources and personalizing marketing. These real-world applications show how businesses are leveraging AI agents to drive efficiency, innovation, and measurable results.
-
Bayer
A pharmaceutical company uses AI agent in drug discovery and disease protection. They use Google search trends for real-time support, location-specific healthcare and manufacturing planning. By implementing agentic AI into the workflow system, the company has streamlined operations and enhanced production efficiency.
-
AES
A global energy company uses a GenAI agent to automate and streamline its energy safety audits. This has reduced audit costs by 99%, increased accuracy by 10-20%, and reduced production time from 14 days to one hour.
-
Walmart
A global retail company implemented an AI agent into their system that automatically prioritizes and recommends tasks, especially during overnight stocking shifts. They have deployed AI agents to its 1.5M U.S. associates to reduce shift-planning time and streamline store work. Their associates use conversational AI to answer onboarding calls, scheduling, or product-location questions. Thus, empowering staff to serve customers rather than getting bogged down searching for procedures.
-
Vodafone
A telecom company uses AI agent to manage around one million daily conversations across more than 15 markets. This advanced technology enabled the company to deliver quick responses and reduce escalations. Automated interactions have improved accuracy, personalization, and customer satisfaction.
-
Uber
A transportation company that uses AI agents to enhance employee productivity, save time and streamline operation. It uses an AI tool that identifies context from previous communication of users to help human agents to resolve issues quickly.
Driving ROI and efficiency: How Needle, an AI agent accelerated client success
Needle, our versatile generative AI framework automates workflow and provides your team context aware AI agents to work smarter. With Needle, organizations can design powerful agents for complex reasoning task execution, and interaction with external data sources.
Our client Dorothy, an AI patent search company, faced numerous challenges in their daily operations. These challenges include managing massive global patent datasets and ensuring the platform could understand and respond to complex, multilingual queries. They faced the following issues:
- Managing multi-language support
- Lack of resources to upload and compare scientific documents
- Handle large scale patent data
Our AI experts tailored a roadmap that incorporates innovative GenAI frameworks like Needle, to enhance operational efficiency and drive value.
Solutions provided using Needle framework:
- Implemented flexible system that routes user queries to multiple model chains.
- A REST API infrastructure was developed to efficiently handle large-scale patent data.
- Analytical tools were integrated into the system, allowing for real-time visualization of results in charts and graphs.
- The platform enabled users from different geographies to query and interact with the system seamlessly in their native language.
We implemented solutions that enabled users to compare uploaded scientific documents with patents. Thus, providing significant value to researchers and legal teams. Moreover, it streamlined the patent analysis and decision-making process.
What is the future of AI agents?
Agentic AI technologies are transforming the way industries function. Multimodal agents are frameworks of multiple autonomous agents interacting in a shared environment to achieve complex goals. Let’s explore how AI agents will evolve in future:
-
Autonomy
Future AI agents will make decisions independently more often. Edge computing will play a vital role. They can be implemented in tasks that need quick action, like in self-driving cars and smart homes.
-
Hyper-personalization
AI will enhance and personalize every task. Multimodal AI agents will look at medical images and patient records, to allow healthcare providers to make better diagnoses. In retail, AI will make shopping for customers more personal, increasing sales revenue. AI agents will also provide personalized financial advice by learning and adapting through experience.
-
Self-improving systems
This AI system will find and fix their own problems, with minimal downtime. They will use methods like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to make their answers more accurate. Self-improvement systems have become vital in fields such as healthcare and finance. Without human supervision, AI agents will work efficiently and at scale.
Accelerate growth by integrating AI agents into your business operations
AI agents are practical and scalable solutions to transform how businesses operate. From automating repetitive tasks to delivering real-time insights and personalized customer experiences, AI agents can boost efficiency and reduce operating costs. By integrating them strategically, organizations can empower their teams, make smarter decisions, and stay ahead in a competitive market. Speed and adaptability define success; AI agents are the competitive advantage you can’t afford to delay.
Take the next step. Integrate AI agents into your digital ecosystem and see how they can simplify complexity and accelerate success.
FAQs
1. What are the 5 types of agents in AI?
The five main types of agents in AI are Simple Reflex Agents, Model-Based Reflex Agents, Goal-Based Agents, Utility-Based Agents, and Learning Agents. Each type differs in how it perceives the environment, makes decisions, and adapts over time. Together, they represent the building blocks for creating AI systems that range from basic automation to advanced, self-improving intelligence.
2. What are examples of AI agents?
AI agents come in many forms, from virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to customer service chatbots that handle queries around the clock. They also include recommendation systems, such as those used by Netflix or Amazon, and autonomous robots in manufacturing or logistics. Each type is designed to perform specific tasks, learn from data, and adapt to user needs.
3. Are AI agents and AI models the same?
No, AI agents and AI models are not the same. An AI model is the underlying algorithm trained to recognize patterns or make predictions, while an AI agent uses one or more models to take action, interact with its environment, and achieve specific goals. In simple terms, the model is the “brain,” and the agent is the “doer.”
4. Are AI agents used in chatbots and virtual assistants?
Yes. AI agents are the core technology powering many chatbots and virtual assistants, enabling them to understand questions, process information, and respond naturally. They use capabilities like natural language processing and machine learning to provide relevant answers, complete tasks, and improve over time based on user interactions.
5. Do all AI agents have the ability to learn?
Not all AI agents have the ability to learn. Some are designed to follow predefined rules and respond only to specific inputs, without adapting over time. Learning agents, however, can improve their performance by analyzing past experiences and adjusting their behavior accordingly.