A smart contract is a computer program stored on a blockchain. It is programmed according to the conditions of a buyer-seller agreement to control the transfer of digital assets among the parties under specific conditions. A smart contract executes automatically when preset conditions are met. By automating agreement execution, smart contracts allow participants to know the outcome as soon as possible without involving an intermediary.
Smart contracts make transactions observable, clear and permanent. They are constantly evolving and exploiting conventional methods of providing financial services in different ways. Smart contracts are similar to traditional contracts. Where a traditional contract is enforceable by law, smart contracts are enforceable by code.
A few facts about smart contracts:
- The bitcoin network used smart contracts for the first time to transfer value from one individual to another.
- The smart contract verifies if the required funds are available in the sender’s account.
- The Ethereum platform enables developers to customize contracts in a Turing-complete language.
- Since the contracts were written in a Turing-incomplete language for the bitcoin network, it restricted the implementation of smart contracts in it.
- The common smart contract platforms are Ethereum, Polkadot, Solana, Hyperledger Fabric, etc.
Let’s discuss smart contracts, their types and how they work
Types of smart contracts
There are three types of self-executing smart contracts based on their applications:
1. Smart legal contracts
These smart contracts are legally enforceable and oblige the parties to fulfill their contractual commitments. In case either of the parties fail to fulfill obligations in the contract, the smart legal contract would automatically trigger legal action against the party that violates the contract.
2. Decentralized autonomous organizations
Decentralized autonomous organizations are blockchain communities. These communities are bound by a set of established rules that are coded via smart contracts. Participants must adhere to the rules of their community and apply those rules to their actions. These rules are built of several smart contracts and work together to keep a check on actions in the community.
3. Application logic contracts
These contracts contain application-based code that is synced with other blockchain contracts. They enable communication via multiple devices, for example, the merger of the Internet of Things (IoT) with blockchain technology. These contracts are essential parts of multi-function smart contracts and usually operate according to a managing program.
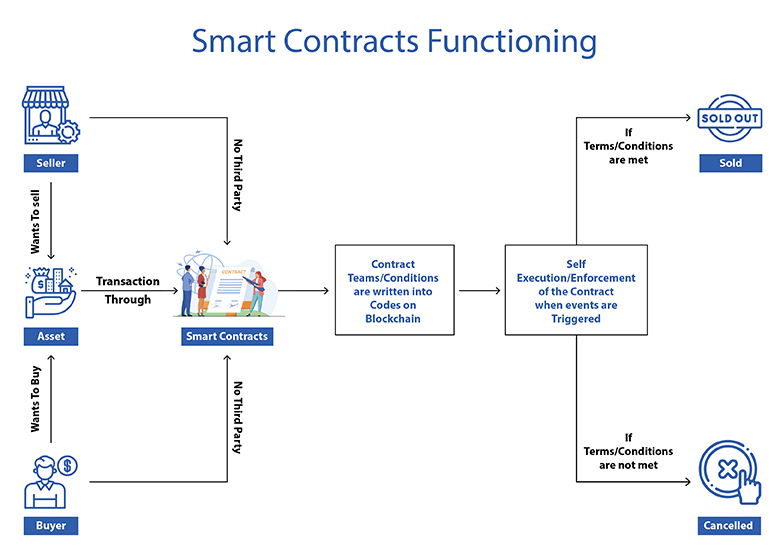
The functioning of a smart contract in a financial transaction
How do smart contracts work?
Let’s understand this with the help of an example. Imagine a situation where you want to buy a property. The purchase would involve multiple expenses, such as bank charges, lawyers’ fees, property dealers’ commissions, etc. However, if you form the agreement on the blockchain using smart contracts, you will easily save money on commissions. You will avoid delays and save the hassle of coordinating with a dealer for processing the agreement.
Moreover, once an agreement is formed using a smart contract, it cannot be altered. Also, once the conditions of the agreement are met, the smart contract executes itself automatically. This removes the need for a third party as mentioned above. This is one example where smart contracts can be easily accessible and executed upon fulfilment of the conditions laid in the agreement.
Imagine smart contracts as digital statements like “if-then” between different parties. If the conditions are met, the agreement is executed, and the contract is marked as complete.
You can bind contracts in executable code instead of traditional paper contracts with smart contract development.
The necessary steps are:
- Transaction initiation from a user’s blockchain wallet
- It reaches the distributed database and its identity is confirmed
- The transaction is approved
- It contains the code that describes the type of transaction
- The transaction is added to the blockchain as a block
Any further change in contract status is updated through the same process.
Global smart contracts market size will surpass USD 1460.3 Mn by 2028 at a CAGR of 24.2%.
-GlobalNewswire
Some common applications of smart contracts are:
Digital identity
Digital identity is established by an individual’s data, reputation and their digital assets. People can learn about an individual without knowing their real identity or validating any transaction using smart contracts. Say, for example, the smooth execution of the ‘know your customer’ process, commonly referred to as KYC, helps to improve flexibility, interoperability, agreement, etc.
High security
The application of smart contracts has simplified the management of capitalization tables. Furthermore, it eliminates intermediaries, including security custody chains. It also supports automatic payments, dividends, liability management, etc.
Loans and mortgages
The use of smart contracts has improved financial services, including loans and mortgages. When the entire loan is repaid, the property can be released. It helps to ensure an error-free process and helps to track payments.
Government
Smart contracts can improve government operations. It includes land title recording, which may ease property transfers for the government. It will also decrease auditing costs and enhance transparency. Smart contracts also make e-elections easier.
Supply chain management
The use of smart contracts makes it convenient for you to monitor items in the supply chain with complete visibility and transparency. It also improves tracking and reduces fraud and theft.
Clinical trials
Smart contracts can greatly assist in clinical trials by enhancing inter-institutional visibility. They can assist in automating data sharing between institutions and facilitate privacy preservation calculations.
The future of smart contracts!
Smart contracts are essential as they bring transparency, time effectiveness, accuracy, security, cost-effectiveness, and trust to transactions. Anyone can create a smart contract and deploy it on the network. They open an extensive range of opportunities to accelerate the adoption of digital transformation.
Smart contracts and blockchain cultivate a distinct category of business relationships based on trust. Unlike traditional business models, blockchain-based storage offers unchangeable and distributed storage as it inherits blockchain properties. This makes smart contracts a trustworthy medium to execute business agreements and financial transactions. Our team of smart contract developers build secure and bug-free smart contracts using Remix, Solidity, Go, JavaScript, and other smart contract development tools. If you’re excited about developing powerful apps centered on blockchain, talk to our experts.