Facial recognition is central to digital identity in banking, retail, healthcare, and travel. By converting facial features into encrypted templates matched in real time, organizations can replace passwords with a glance, streamlining customer journeys and enabling contactless experiences.
KPMG’s 2023 Global Banking Fraud Survey found that firms using multimodal biometrics such as facial recognition reduced account takeover fraud by 66% within one year of implementation. Facial recognition also powers computer vision applications that streamline complex visual processes and provide real-time analytics.
Facial recognition delivers its full potential when guided by clear strategy, experienced advisors, and smooth integration. A seasoned technology partner can give expert guidance regarding vendor selection, data stewardship, compliance and back-end connections.
In this blog post, you will see the business value of facial recognition, the mechanics behind the technology, proven industry examples, an overview of core detection techniques, and a practical deployment plan.
From image to identity: AI facial recognition explained
AI facial recognition uses advances in machine learning and computer vision to identify individuals in images and video. The process unfolds in three stages: detection, feature mapping, and matching. Each stage transforms raw image data into actionable identity information.
Stage 1: Detection
A camera or sensor captures an image or video frame. A convolutional neural network then locates faces by drawing bounding boxes around each face region in real time.
Stage 2: Feature mapping
Once detected, the system extracts key landmarks such as eye corners, nose tips and mouth edges. It encodes these into a numeric vector called a faceprint, which captures the unique geometry and texture of each face.
Stage 3: Matching
When a faceprint is ready, the system searches its database of enrolled templates to identify the best match. It evaluates how well each stored record aligns with the new print and ranks the candidates by confidence. When the top candidate meets the required confidence level, the system confirms the person’s identity. This approach supports both one-to-one verification and broader one-to-many searches.
Detection, feature mapping and matching depend on reliable face detection techniques to maintain accuracy under real-world conditions. Together, these stages form a robust pipeline that powers applications from secure access control to seamless customer interactions.
The business impact of face recognition solutions
Facial recognition transforms identity checks into strategic levers for security, efficiency and business intelligence, delivering measurable gains across operations. Here are its core benefits:
1. Enhanced security
Since biometric markers are unique and cannot be shared, they make unauthorised entry much harder than stolen cards or guessed passwords.
2. Contact-free authentication
A touch-free sign-in removes shared surfaces and speeds the experience for every user.
3. Accelerated user workflows
Instant face matching can shrink verification time to under a second, so that companies can streamline processes such as customer onboarding and gate access.
4. Lower operational costs
Automated verification reduces manual checks, paperwork and staffing, delivering long-term savings on labor and administration.
5. Actionable analytics
Every authentication event generates data on user behavior, location and device patterns, enabling continuous service improvements and personalization.
6. Significant fraud reduction
Deployments have delivered account-takeover fraud drops averaging 66 percent within 12 months and up to 90 percent in specific cases such as a major bank’s pension-program rollout.
7. Elastic scalability
Cloud-native platforms can manage millions of stored templates and ramp capacity instantly to handle peak loads without performance degradation.
These advantages translate into real-world results across diverse sectors.
Applications of facial recognition across industries
Facial recognition drives measurable gains in safety, customer service and operational efficiency. The six examples below show how different industries put the technology to work.
1. Security and law enforcement
Law enforcement agencies continuously scan live video and images to detect faces in real time. They match those detections against watchlists and missing-person records. This accelerates suspect identification, supports prompt intervention, and strengthens public safety.
In a pilot program including body-worn cameras and CCTV, South Wales Police cut average identification time from fourteen days to fewer than five minutes.
2. Retail
Retailers install recording devices of the facial-recognition system at various entry points and self-service kiosks. This helps identify registered loyal customers instantly, allowing tailored promotions, analysis of periodic footfall and reduced shrinkage.
China recorded 495 million face-payment users in 2021, enabling cashier-less checkout and lifting adoption by 15 percent year on year.
3. Healthcare
Hospitals place face-scanning kiosks at admissions desks, pharmacy counters and ward checkpoints. Automated patient ID prevents record mix-ups, tracks staff compliance and cuts medication errors to under a minute.
A hospital in Hangzhou raised ID accuracy to 99.80 percent and reduced registration time to 30 seconds for 200,000 annual visits.
4. Finance
Banks use facial recognition for digital account opening and ATM access, embedding it into transaction approvals. This streamlines onboarding, adds a biometric layer to authentication and instantly flags anomalies to cut fraud.
In 2021, National Australia Bank’s smartphone face-ID system reduced remote account fraud by 30 percent and shortened new-customer onboarding from days to under ten minutes.
5. Events and hospitality
Event venues and hotels deploy facial recognition at gates and service desks to deliver contact-free check-in and personalized guest experiences. The technology speeds entry, manages VIP flows and strengthens security without manual ID checks.
Carnival Cruise Line’s biometric kiosks across nine U.S. homeports accelerated guest debarkation by 30 percent while maintaining a 98 percent match accuracy rate.
6. Smart cities
Transport authorities can integrate face recognition into ticketing, public kiosks and security cameras to verify passengers, automate fares and spot persons of interest.
Hangzhou’s City Brain platform uses roadside face-recognition cameras to adjust traffic lights in real time, cutting congestion by fifteen percent.
Face-detection techniques and technology stack
False positives undermine confidence and missed detections expose vulnerabilities. Combining geometric methods with deep-learning models ensures accurate spotting across lighting and angles, giving teams the confidence to scale biometrics. Below are the five essential face-detection techniques that deliver this reliability:
1. 2D geometric methods:
Early systems locate patterns such as skin tone and edges or apply Haar cascades to find facial regions. They run quickly on basic hardware but struggle under varied lighting and complex backgrounds.
2. 3D structured-light scanning:
This technique projects infrared patterns (known as structured-light dots) onto the face to capture depth information. It delivers robustness against angle changes and spoofing but requires specialized cameras and additional processing power.
3. CNN-based detectors:
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) trained on extensive face datasets detect people across varied poses and lighting. They run in real time on edge devices and form the core of most production-grade systems.
4. Liveness checks:
To prevent spoofing with photos or masks, systems analyze subtle cues such as eye movement, head motion, or skin texture patterns from video frames. Liveness modules may be software-only (for example, blink detection) or hardware-assisted (using infrared pulse sensing).
5. Privacy by design features:
Advanced solutions support on-device face matching, template encryption and configurable data retention settings. This design keeps raw images local and converts biometric data into irreversible, privacy-safe templates.
Layered correctly, these components form a robust face-detection stack that delivers speed, accuracy, and security without compromising user privacy.
Roadmap to deploy facial recognition
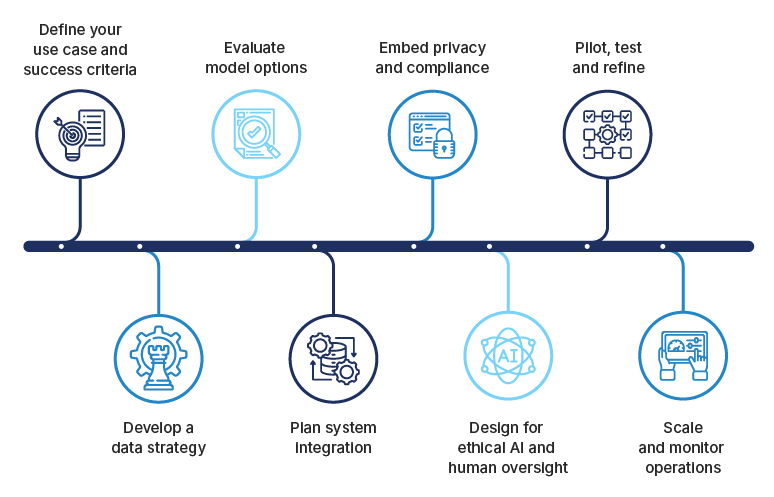
A well-executed facial-recognition deployment can reduce fraud, streamline operations and ensure compliance while safeguarding user trust. Use this step-by-step process to deploy robust, ethical and high-impact facial recognition solutions:
Step 1: Define your use case and success criteria
Begin by defining clear objectives, such as touchless onboarding or secure site access. Then set measurable targets for accuracy, response time, and user satisfaction. Finally, link those targets to outcomes like reduced fraud and lower verification costs.
Step 2: Develop a data strategy
Begin by reviewing image and video sources to confirm coverage across all relevant demographics and environments. Implement consistent processes for data labeling, preprocessing, and secure storage. Schedule regular updates that cover data augmentation and quality assessments to keep your dataset current and reliable.
Step 3: Evaluate model options
Compare commercial APIs, open-source libraries and specialized face detection services against your data. Assess accuracy, bias mitigation, liveness-detection support and total cost of ownership. Review vendor roadmaps and update cycles.
Step 4: Plan system integration
Design how facial recognition fits into identity management, access control and analytics platforms. Define APIs, message queues and infrastructure to handle real-time matching or batch processing without disrupting workflows.
Step 5: Embed privacy and compliance
Each facial-recognition system must implement safeguards to protect an individual’s personal data. The technology should be used responsibly by ensuring proper consent is obtained, data is handled responsibly to uphold customer trust, and anonymization and encryption techniques are applied to prevent misuse. Security practices must comply with GDPR and the rules and regulations of other relevant bodies.
Step 6: Design for ethical AI and human oversight
Integrate explainability features into your detection pipeline. Pair these with human-review checkpoints to catch and correct anomalies. Then map out workflows for edge cases and define clear escalation paths to address false positives or negatives promptly.
Step 7: Pilot, test and refine
Run a pilot in a representative setting and track performance against KPIs while collecting user feedback. Identify edge cases, tune thresholds, retrain models with fresh data and update policies before scaling.
Step 8: Scale and monitor operations
Once the solution is live, use dashboards to track accuracy, processing speed and fairness metrics. Conduct regular bias and performance audits to detect drift early. Expand infrastructure as needed to maintain resilient performance under peak loads.
Eliminate fraud gaps and streamline access
High fraud losses and growing check-in lines show where passwords and swipe cards fall short. A sound facial-recognition rollout starts with a targeted audit of failure points. Setting measurable goals for fraud reduction and throughput provides a clear evaluation framework. A focused pilot then validates accuracy, privacy controls and human review workflows before full deployment. The insights gained here build a solid foundation for enterprise-wide adoption.
Navigating strict privacy rules and complex legacy systems calls for an experienced guide who can shorten timelines while keeping compliance on track. Softweb Solutions pairs privacy-first engineering with proven integration patterns, embedding facial recognition into existing platforms without disrupting operations. Connect with us today to see how our tailored face detection services lower fraud rates and optimize access flows.
FAQs
1. How does facial recognition improve security beyond traditional methods?
Facial recognition relies on unique physical features that cannot be copied or shared, like cards or passwords. By analyzing dozens of facial landmarks in real time, it confirms identity with a level of precision that makes stolen credentials and impersonation far less likely.
2. Why is high accuracy in face identification crucial for security applications?
High accuracy ensures genuine users are granted access without friction while potential intruders are flagged reliably. Clear approvals and reliable rejections inspire trust and keep workflows running smoothly.
3. What are the main challenges to implementing facial recognition systems?
Facial recognition systems face three core hurdles during implementation: accuracy, bias, and privacy. Variations in lighting, camera angles, and simple obstructions can cause the system to miss faces. Training data that does not include all user groups equally may lead to more errors for certain people. Collecting and storing biometric information also requires clear user consent, strong encryption and transparent usage policies.
4. How much can businesses save operationally with facial recognition technology?
By automating identity verification, companies can eliminate tedious manual checks, cut staffing and paperwork expenses, and allow teams to focus on more strategic work.
5. In what ways does contactless authentication benefit healthcare and public spaces?
Contactless face scans remove shared touchpoints and shorten lines, improving hygiene and speed. In hospitals, patients move through registration and pharmacy faster and more safely. In public venues, visitors enjoy quicker entry while distancing guidelines remain intact.