Next.js is a versatile framework with built-in features suitable for modern web development. It has emerged as a powerful tool providing support to the developers for creating high-performance web applications. On the other hand, React.js helps to create a robust and interactive user interface. Next.js facilitates the capability by offering server-side rendering, static site generation, and streamlined routing out of the box. In this blog we will discuss the differences between Next.js and React.js technologies, their features, use cases and pros and cons in detail.
What is Next.js?
Next.js is a robust open-source framework specifically designed to work with React to build fast and user-friendly web applications and static websites. It simplifies web app development and offers built-in server-side rendering, static site generation, and automatic code-splitting features. It also provides a set of conventions and tools to streamline tasks. To fully leverage the potential of Next.js, hire React.js developers who can bring their expertise to create seamless and efficient applications.
Let us start with what’s in Next.js?

- Built-in optimizations – Automatic optimizations of image, fonts, and scripts for improved UX and core web vitals.
- Dynamic HTML streaming – Stream user interface (UI) instantly from the server, integrated with the app router and react suspense.
- React server components – Add React components without sending additional JavaScript to the client side built on the latest React features.
- Data fetching – js supports both server and client data through the React component.
- CSS support – Style your applications with tools including CSS Modules, Tailwind CSS, and popular community libraries.
- Client and server rendering – Flexible rendering and caching options including Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR) per page.
- Server actions – Run server code by calling a function and easily revalidate cached data and update your UI.
- Route handlers – Build API endpoints and securely connect with third-party services for handling authentic webhooks.
- Advanced routing and nested layouts – Create routes, including support for more advanced routing patterns and UI layouts using file systems.
- Middleware – Take control of the incoming request and use code to define the route. Also access rules for authentication, experiment, and internationalization.
Key features of Next.js
Routing
- Automatic page routing: js provides a file-based routing system where each file in the pages directory automatically becomes a route. This simplifies development, enabling faster time-to-market for web applications.
- Dynamic routing: Businesses can create dynamic routes for personalized customer experiences, such as unique product pages, user dashboards, or tailored content.
- API routes: Build serverless API endpoints directly in your application, reducing reliance on external APIs and improving integration speed.
Rendering
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Ensures your web pages are fully rendered on the server before being sent to the user, improving SEO and initial page load times—critical for driving organic traffic and customer retention.
- Static Site Generation (SSG): Generates pages at build time, ideal for delivering lightning-fast, static content like blogs or landing pages, reducing hosting costs.
- Client-Side Rendering (CSR): Enables interactive, dynamic user experiences, such as real-time updates or dashboards, enhancing user engagement.
Data fetching
- getStaticProps: Fetches data at build time for static pages, ideal for content that doesn’t change often, ensuring fast loading and reduced server load.
- getServerSideProps: Fetches data at request time, perfect for applications requiring dynamic or frequently updated content, like e-commerce product listings or personalized offers.
- Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR): Allows businesses to update static content in real-time without rebuilding the entire application, enabling scalability for high-traffic scenarios.
Styling
- Built-in CSS and Sass support: Simplifies styling with native CSS modules, allowing teams to quickly develop visually appealing designs.
- Support for CSS-in-JS libraries: Seamlessly integrates with libraries like styled-components or Emotion, enabling modular and reusable styling, which reduces development time and ensures consistent branding.
- Global styling capabilities: Helps maintain uniform brand identity across the application, reinforcing trust and familiarity with users.
Optimization
- Image optimization: Automatically optimizes images for different screen sizes and resolutions, enhancing user experience and reducing bounce rates.
- Code splitting: Automatically splits JavaScript code by page, ensuring users only download what’s needed, improving site speed and customer satisfaction.
- Built-in analytics: Provides insights into application performance and user behavior, enabling businesses to make data-driven improvements.
TypeScript
- Strong typing: Minimizes bugs by catching errors during development, ensuring a more robust and reliable application.
- Ease of adoption: js comes with built-in TypeScript support, allowing development teams to transition seamlessly and write maintainable code.
- Scalability: Ensures code quality and consistency, making it easier for businesses to scale applications and onboard new developers.
Suggested: How can JavaScript revolutionize your backend with the top frameworks
Pros of using Next.js
Improve search engine optimization
Create and maximize the potential of your web application with all the features and interactivity required, ensuring optimal search engine visibility like a static text-based website. Gain a competitive edge with this strategic approach.
Open graph customization
Single page applications make it challenging for effectively displaying metadata for each URLs within your web applications. It optimizes SEO and improves the appearance of your URL on social networks.
Enhance performance
It mitigates the browser stalling caused by downloading and simultaneously executing large JavaScript code, resulting in improved metrics such as total blocking time (TBT). It also monitors the time duration at which the script blocks the user interaction with the web app. If your TBT is higher, the visibility of your web app to the users increases.
Lazy loading
Next.js provides better user experience. For example, if your website takes time to load then it might happen that the user will exit from the website. So, you need to employ a tool such as a spinning wheel for the user to understand that the page is loading.
Accessibility
Next.js webpages are cross-platform compatible, making them widely accessible.
Cons of using Next.js
Routing
Next.js is limited to some projects and is used only for file routers. If you need to use dynamic routes, you need a Node.js server.
Build time
Next.js supports the static structure of the entire website content. Further, creating apps with multiple pages can be time-consuming.
Differences between React.js and Next.js
| Parameters | Next.js | React.js |
|---|---|---|
| Type | It is a framework built on top of React. | It is a JavaScript library for building user interface. |
| Rendering | Supports client-side, server-side rendering, and static site generation (SSG). Extremely fast rendering. | Supports client-side rendering. |
| Dynamic routes | Automatic handling | Manual configuration |
| Features | Automatic code splitting, CSS support, TypeScript support | Core functionality for building UI components. |
| Documentation | Learn-by-doing tutorials like component creation, development, integration, and guiding. | Similar design – few introductory activities to explain fundamentals. |
| Routing | Built-in file-based routing | No built-in router |
| Code splitting | Automatic for optimized performance | Manual configuration |
| Learning curve | Complex | Simple |
| API routes | Integrated API routes for serverless functions | Typically handled separately in the backend |
| Static site generation | Supported for faster page load | Not supported |
| Deployment options | Simplified deployment, often using serverless platforms | Can be deployed to various hosting solutions |
| Development server | Built-in development server with HMR | Requires additional configuration for server setup |
| Error handling | Comprehensive error handling & custom 404 pages | Manual error handling with components |
| Authentication | Integrated solutions for authentication | Requires integration with third-party libraries |
| Community and support | Small yet growing community | Large and active React community |
Why should you use Next.js?
There are various benefits of Next.js:
- Increased sales and conversion rate
- Enhanced marketing channels
- Reduced maintenance cost
- Improved user experience
- Easier business scaling
- Gives a competitive edge
Real-world uses of Next.js
- Netflix – The server-side rendering framework capabilities are important in delivering a smoother streaming experience.
- WhatsApp – The server-side rendering framework can handle dynamic content that facilitates real-time display of messages and updates providing users a reliable communication platform.
- Spotify – js allows faster page loads and enhances the user experience when accessing music.
- Uber – The framework supports for incremental static regeneration, enabling the delivery of up-to-date information whether booking a ride or checking updates on journey.
Some of the key advantages are:
- Facilitates the creation of web applications with server-side render and static website
- Enhances performance and SEO
- Optimizes user experience
- Built-in routing and API handling
Let us explore React.js now
React.js is an open-source JavaScript library used for building dynamic and interactive user interfaces for web applications. Maintained by Meta (Facebook), it is primarily used for managing the view layer in the Model-view-controller (MVC) architecture. React.js excels at creating reusable UI components and ensures high performance with its virtual DOM implementation. It supports the development of scalable, fast, and modern web applications by simplifying complex UI development tasks.
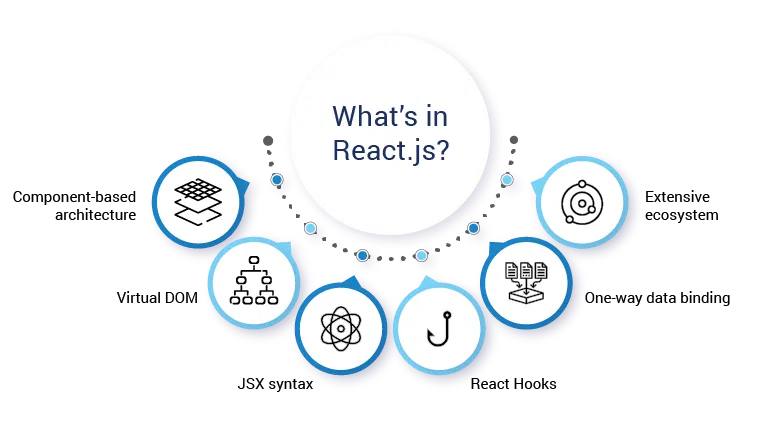
What’s in React.js?
- Component-based architecture– Modular and reusable components for maintainable codebases.
- Virtual DOM– Optimized updates for improved rendering speed.
- JSX syntax – A mix of JavaScript and HTML for a streamlined development experience.
- React Hooks – State and lifecycle management in functional components.
- One-way data binding – Ensures a predictable and debuggable data flow.
- Extensive ecosystem – Offers tools, libraries, and community resources for various development needs.
Key features of React.js
- Declarative syntax:Write code that describes what the UI should look like, and React.js handles the updates.
- Reusability:Create components that can be reused across different parts of the application.
- Virtual DOM:Ensures efficient rendering for dynamic applications.
- Flexibility:Easily integrates with other libraries or frameworks.
- Developer tools:Powerful debugging and profiling tools available through browser extensions.
Pros of using React.js
- Efficient rendering: The virtual DOM boosts performance, especially in large-scale applications.
- Reusable components: Reduces code duplication and improves maintainability.
- Strong community: Thousands of open-source libraries and strong documentation support.
- Cross-platform development: Extend capabilities to mobile app development using React Native.
- SEO optimization: Pair with server-side rendering solutions for better search engine visibility.
Cons of using React.js
- Steep learning curve:New developers may find JSX, hooks, and advanced state management, challenging.
- Incomplete framework:js only provides the UI layer; other libraries are needed for state management and routing.
- Frequent updates:The rapid pace of updates requires constant learning to stay up to date.
- Overhead for small projects:May be overkill for simpler applications.
Why should you use React.js?
- Delivers high performance for applications requiring frequent updates.
- Offers reusable components for faster development cycles.
- Provides flexibility to integrate with third-party libraries.
- Ensures a stable and predictable codebase with one-way data binding.
- Offers strong community support for problem-solving and resource sharing.
Real-world uses of React.js
- Dynamic dashboards:Powering real-time analytics dashboards in industries like finance and e-commerce.
- Social media applications:Facebook and Instagram use React.js for building interactive features.
- Single-page applications:Platforms like Airbnb and Trello rely on React.js for seamless navigation.
- E-commerce websites:Walmart and Shopify use React.js to manage product pages and user interactions.
- Video streaming platforms:js enables dynamic interfaces for personalized user experiences on Netflix.
- Educational platforms:Platforms like Khan Academy leverage React.js to build interactive learning interfaces.
React.js vs. Next.js: Choosing the right framework for your web development needs
Choosing between React.js and Next.js depends on your specific requirements:
- Opt for React.js if you need a customizable and flexible library for building front-end applications.
- Choose Next.js if you want a full-stack framework with built-in optimizations and advanced rendering capabilities.
Evaluate your business goals, project complexity, and resource availability to decide which technology aligns best with your needs. Do you want to elevate your web application with top JS frameworks and unlock new possibilities? Talk to our experts.
FAQ’s
1. Is Next.js better than React?
Next.js and React serve different purposes depending on application needs. React is well suited for building flexible, client-side user interfaces, while Next.js extends React with server-side rendering, routing, and performance optimizations. The choice depends on whether the project prioritizes UI flexibility or full-stack delivery and SEO.
2. What is the main difference between React and Next.js?
The main difference between React and Next.js is that React is a UI library, while Next.js is a full framework built on React. React focuses only on building interfaces. Next.js adds routing, server-side rendering, and deployment features, making application development more structured.
3. Why is React more popular?
React is more popular because it is flexible, lightweight, and backed by a large developer community. It allows teams to choose their own tools for routing, state management, and data handling. This adaptability makes React suitable for a wide range of front-end projects.
4. Which framework is better for large-scale projects?
Next.js is better for large-scale projects that need performance, SEO, and scalability. It provides built-in routing, rendering strategies, and optimization features. These capabilities reduce architectural decisions and help teams manage complexity as applications grow.
5. Can I start with React and migrate to Next.js later?
Yes, you can start with React and migrate to Next.js later because Next.js is built on React. Most existing React components can be reused with minimal refactoring. This allows teams to begin with client-side rendering and later adopt server-side rendering and built-in optimizations as requirements evolve.