Delivering flawless products starts with implementing the right quality checks. Visual inspection ensures products, systems, and equipment are thoroughly examined for visible defects, helping businesses maintain reliability and safety across industries.
AI-driven systems enhance defect detection accuracy, and provide organizations with cost-efficient, reliable, and adaptable inspection methods that meet diverse operational needs. Visual inspection improves defect detection accuracy by identifying flaws early, reducing rework and waste, which lowers overall production costs.
According to McKinsey, implementing AI-powered visual inspection has improved defect detection and accuracy by 90% using deep-learning-based systems.
Automated visual inspections are becoming more precise, minimizing human errors and enhancing defect detection in complex, high-volume environments. In this blog post, we will explore what visual inspection is, its importance, benefits, the different types of defect detection, techniques, and tools that make it effective.
What is visual inspection?
Visual inspection is a systematic approach that detects defects in product structures and components through the use of devices to evaluate their quality and integrity. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) is a method of testing materials, systems, or components without causing any damage. In NDT, visual inspection is the front line of defense. It is an initial evaluation compared to other NDT methods, where advanced methods like ultrasonic or radiographic inspection are adopted only after visual inspection.
In the past, it literally entailed directly scrutinizing an object or process to find defects or deviations from standard requirements. Presently, organizations employ high-definition cameras, drones, and digital equipment to take pictures and videos of machinery, products, and physical assets to inspect them. This change allows for the quicker detection of defects, improved safety when operating in dangerous environments, and more uniform quality checks, ultimately lowering downtime and inspection expenses.
A survey conducted by Gartner predicts that 20% of respondents have already adopted AI-enabled vision inspection systems.
Why is visual inspection important for defect detection?
Visual inspection provides assurance for safety, product quality, and compliance with regulatory requirements through the proactive identification of defects and hazards. It serves as the first line of defense in quality control and maintenance across industries. Businesses can detect issues at an early stage before they become big challenges.
-
Maintains quality control
Detection of faults such as cracking and discoloration at the initial stage of production enables businesses to implement corrective actions. This enhances the quality of goods before they reach customers. Thus, avoiding the delivery of faulty products to customers.
-
Ensures safety
Visual inspection immediately finds out physical harm or potential danger in equipment and building locations. Companies can act proactively, ensuring a safer working environment and avoiding accidents. This is especially critical in industries like manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive, where safety risks can have severe consequences.
-
Guarantees compliance
Industries operate under strict regulations. Regular visual inspection guarantees that the process and equipment meet industry requirements. Aligning procedures with relevant regulatory standards prevents companies from facing penalties and legal problems tied to non-compliance.
-
Brand reputation and trust
Consistent product standards help prevent products from being faulted and ensure that they serve their intended purpose. This assists companies in building customers’ trust and loyalty. Additionally, it reflects an organization’s dedication to quality, generating long-term trust, repeat business, and better positioning in competitive markets.
What are the benefits of adopting visual inspection services?
Visual inspections are non-destructive and a foundational component for ensuring regulatory compliance and customer satisfaction. It has emerged as a transformative force that revolutionizes and streamlines the operating process. Here are the benefits that enhance both operational processes and end-user satisfaction.
-
Cost-effective
Businesses use visual inspections to prevent defective products from reaching customers. Thus, it reduces waste and costs. Visual inspection is also carried out with minimal tools. This makes it cost-efficient compared to other forms of inspection. Businesses can plan better and have higher returns without sacrificing safety and quality standards.
-
Fast and efficient
Identifying issues in advance using visual inspection allows companies to correct issues in time. This shortens downtime and improves the working process. Visual inspection systems can assist companies in minimizing downtime and achieving market needs without compromising on accuracy or reliability.
-
Optimization
Visual examinations are fast and inexpensive methods of inspecting quality levels without placing a heavy burden on workload. Implementing automated visual inspection organizations can optimize manufacturing processes, minimize human intervention, and simplify workflow. Such optimizing of processes on a continuous basis minimizes waste, maximizes productivity, and fosters long-term operating efficiency for manufacturing and quality control processes.
-
Accuracy
The use of automated inspection generates more precise results compared to human sight. AI can detect minor flaws that are quite easy to overlook by performing human inspections. This improves accuracy, provides consistent quality, and enhances industry standard compliance. Detecting defects accurately supports brand reputation and customer faith.
What are the different types of visual inspections used across industries?
Visual inspection is a non-destructive test that relies on human senses to detect material, structure, and equipment defects. Advances in technology such as artificial intelligence and machine learning have improved the accuracy and consistency of inspections. The most common ones are outlined below.
-
Direct visual inspection
In this technique, all the products are visually inspected by skilled experts. Here, the inspectors inspect objects or product surfaces using simple inspection tools or the naked eye. The method is very labor-intensive and demands repetitive operations. This is most prevalent in sectors with rapid, hands-on evaluations.
Requirements:
- Trained inspectors are required to minimize human error and fatigue
- Standardized inspection protocols are necessary to maintain consistency across facilities.
- High-quality lighting, magnification tools, and specialized equipment are required to detect micro-defects in complex components.
Benefits:
- Simple to set up and requires minimal equipment or training
- Flexible for inspecting a wide range of items on the spot
- Low upfront cost compared to technology-driven solutions
Tools used: Flashlights, mirrors, magnifying glasses, and surface rulers
-
Remote Visual Inspection (RVI)
With the help of robotic systems, drones, and edge technology, companies can perform visual inspection at a distance or from remote locations. This technique can be applied to high-temperature areas, narrow spaces or underwater. Remote visual inspection can be performed by capturing images and inspecting them later. This technique improves visual accuracy and safety, and efficiency.
Requirements:
- Requires trained operators and specialized equipment
- Adequate lighting and unobstructed access to maintain clear visibility
- Regular maintenance of inspection equipment to keep systems functioning at best level
Benefits:
- Enables safe inspection of hazardous or hard-to-reach areas
- Reduces downtime by eliminating the need for full system disassembly
- Provides detailed visual data for documentation and long-term analysis
Tools used: Robotic crawlers, UAVs with HD cameras, and underwater ROVs
-
Automated visual inspection
Companies conduct visual inspection with the aid of AI, machine learning, and computer vision. Surface of objects and products are scanned in real-time by cameras, drones, and sensors. These technologies are trained to detect anomalies using algorithms. Such a technique is applied in high-production industries where accuracy is paramount.
According to McKinsey, by implementing advanced image recognition techniques for visual inspection and fault detection, productivity can increase up to 50%.
Requirements:
- High initial investment in technology and integration
- Large quality datasets to train and optimize AI models
- May need skilled professionals for setup, monitoring, and maintenance
Benefits:
- Consistent, high accuracy, and reliable defect detection without human fatigue
- Faster inspection of large volumes, reducing cycle times
- Scalable and easy to standardize across multiple production lines
Tools used: High-resolution cameras, robotic arms, and image processing software
Table comparing traditional, remote and automated visual inspection
Selecting the appropriate inspection technique can be difficult, particularly in regard to cost, accuracy, and operational effectiveness. The following is a summary of traditional, remote, and automated inspection and how each provides value and addresses its shortcomings.
| Aspect customers care about | Traditional inspection | Remote inspection | Automated inspection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy of defect detection | Relies on human judgment, higher chance of oversight | Improved accuracy with expert access, but still human-dependent | High precision with AI/ML algorithms, minimizes errors |
| Safety for inspectors | Requires physical presence in hazardous areas | Inspectors can work off-site, reducing exposure | No human presence needed in dangerous zones |
| Inspection speed | Time-consuming manual checks | Faster than traditional due to remote access | Real-time detection and analysis, fastest option |
| Cost efficiency | Lower upfront cost but higher long-term due to errors/rework | Reduced travel and downtime costs | Optimizes resources, reduces rework and operational costs |
| Scalability | Difficult to scale across multiple sites | Easier to scale with remote connectivity | Highly scalable, ideal for large or complex operations |
| Data and reporting | Limited documentation, manual reporting | Complete digital documentation, remote sharing | Automated reporting with detailed analytics and insights |
| Best for | Simple, low-risk inspections | Sites requiring expert review without travel | High-volume, high-precision, safety-critical inspections |
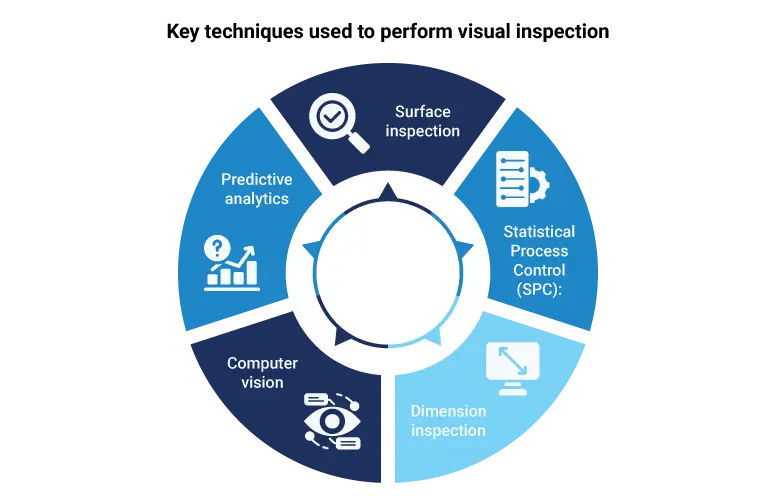
What are the key techniques used to perform visual inspection?
Visual inspection guarantees that products and systems meet established standards and yield accurate results at each level of production. From identifying surface defects to employing computer vision powered by AI, it assists companies in ensuring consistency and minimizing errors. Let’s explore the most commonly employed techniques that make visual inspection solutions an effective tool for quality control.
-
Surface inspection
It detects flaws like scratches and cracks on product or equipment surface. Traditionally surface inspection was done manually. With AI-based image-processing algorithms and high-resolution cameras, it is now easy to detect even the finest of flaws.
Example: In the automotive sector, AI-based surface inspection identifies small scratches, dents, or paint flaws on cars to certify that the car passes both quality and aesthetic checks.
-
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
This method uses statistical techniques to control and monitor processes and enables employees to spot variations and take corrective actions to maintain the product quality. Integrating automated visual inspection with SPC offers real-time monitoring. This enables businesses to act quickly to enhance the product standards.
Example: In manufacturing, product quality can be continuously monitored to ensure proper texture and color are maintained across production runs by implementing AI with Statistical Process Control (SPC).
-
Dimension inspection
Companies measure the size, shape, and orientation of products in dimension inspection to conform to the design specification. This is facilitated by automated inspection systems with optical instruments and laser scanners. Automated dimension inspection increases the speed of production, accuracy, and eliminates human error.
Example: Dimension inspection in semiconductor manufacturing verifies that microchips have precise measurements, allowing them to integrate seamlessly into electronic devices.
-
Computer vision
AI algorithms are employed in computer vision methods to scrutinize visual information. It further identifies patterns and abnormalities that may elude human detection. This process enhances quality control by applying AI-powered visual inspection. Thus, enhancing speed and accuracy. Additionally, the process allows companies to minimize waste, enhance product quality, and boost overall efficiency.
Example: In the food sector, computer vision technology can be employed to inspect foreign bodies, contaminants, and packaging faults in real-time, streamlining the inspection process.
-
Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics employs historical data and machine learning to predict possible defects. This method enables companies to pre-inspect quality and plan proactive maintenance. Therefore, it reduces unplanned downtime and increases the asset’s lifespan.
Example: Predictive analytics in aerospace manufacturing foresees wear and tear in advance so that it can be undertaken in a timely manner before issues arise.

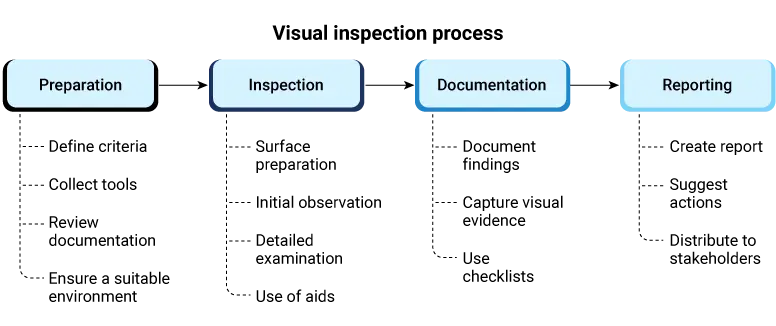
Step-by-step process to implement visual inspection solutions
Visual inspection solution deployment requires an organized, unambiguous approach to achieve efficiency and accuracy. The step-by-step methodology enables companies to use the appropriate tools, automate processes, and get consistent outcomes.
-
Preparation
- Define criteria: Create a clear roadmap that shows what comprises a defect or non-compliance for the items being inspected.
- Collect tools: Ensure all the necessary tools, such as magnifying glasses, mirrors, high resolution cameras, robot arms, and drones, are available and in good condition.
- Review documentation: Read relevant manuals, standards, and previous inspection reports to understand the requirements for implementing visual inspection.
- Ensure a suitable environment: Make sure the environment you’re inspecting is clean and well-lit to provide clear visibility.
-
Inspection
- Surface preparation: Make sure the object’s and equipment’s surfaces are free from dirt. Clean off the grease, contaminants, or dirt that may conceal defects.
- Initial observation: Make an overall observation of the object or system to check for evident problems.
- Detailed examination: Investigate detailed areas or components carefully using a checklist or known procedure.
- Use of aids: Utilize equipment like a high-resolution camera, drones, magnifying lens, mirrors, and special light to increase visibility in inaccessible or difficult areas.
-
Documentation
- Document findings: Write a note of all observations with a detailed description of compliant and non-compliant implementation.
- Capture visual evidence: Make sure to take clear photos or videos of the issues identified to examine later.
- Use checklists: Apply standard checklists for documentation in order to maintain consistency and completeness in reporting observations.
-
Reporting
- Create report: Summarize the findings and point out major issues that must be addressed in a clear and concise manner.
- Suggest actions: Point out and recommend corrective action that must be taken to resolve the issues found.
- Distribute to stakeholders: Prepare and share the reports that need to be shared with relevant personnel for review and action.
What are the common challenges in manual visual inspection?
While visual inspection quickly identifies defects maintaining product quality, there are a few challenges that need to be addressed with the right solutions. This ensures inspection delivers consistent, reliable results.
-
Human error and fatigue
- Challenge: Manual inspections heavily rely on an inspector’s concentration and judgment, which can lead to oversight, especially during repetitive tasks.
- Solution: Adopt AI-powered visual inspection services to reduce reliance on manual checks. Automation ensures consistent accuracy and minimizes the risk of fatigue-related mistakes.
-
Limited detection of subtle defects
- Challenge: Small cracks, surface irregularities, or hidden defects are often missed during traditional inspections.
- Solution: Use high-resolution cameras, advanced sensors, and deep learning algorithms that enhance defect detection and recognize even minute irregularities.
-
Safety risks in hazardous environments
- Challenge: Inspectors working in high-risk areas such as oil rigs, construction sites, or manufacturing plants may face safety hazards.
- Solution: Implement remote and automated inspection systems, including drones and robotics, to carry out inspections without exposing human inspectors to dangerous conditions.
-
Inconsistent reporting and documentation
- Challenge: Manual inspections often lead to subjective assessments and incomplete reporting, making it hard to track long-term quality trends.
- Solution: Integrate digital inspection tools that automatically record, store, and analyze inspection data, ensuring standardized reporting and easy traceability for audits.
Strengthen operational excellence through visual inspection
Visual inspection is no longer just about detecting defects. It’s about building trust and resilience in every stage of operations. By ensuring consistent quality, safeguarding compliance, and protecting brand reputation, AI-driven inspection systems position businesses to compete with confidence in demanding markets. The true value lies not only in operational gains but in securing long-term customer loyalty and industry leadership.
According to McKinsey & Company, by implementing visual inspection systems, businesses have achieved a 40% increase in first pass yield, reducing rework rates by 5%.
Embracing these innovations ensures that businesses stay ahead of quality demands while unlocking significant gains in productivity and profitability.